REST: It's All About Semantics
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
In this post I would like to put my two cents in and talk about RESTful web services. First of all I don't intend to discuss the history of RESTful services. Neither this is a tutorial about implementing RESTful web services. What I'm trying to do is discuss how we, as developers, should think about a RESTful web service and do better RESTful APIs.
First of all I want to thank my friend, Filipe (@filaruina) whom worked with me at Cortex Intelligence. We talked a lot about REST and he helped me to open my eyes to a lot of aspects that I hadn't yet.
There and back again
This month I started working in a new company. One of my first tasks was to finish the integration of two systems which the communication was done via SOAP. When I started reading the source code I saw the common mistake some developers make (including me).
The first thing we do is replace all the SOAP calls by HTTP requests. After that we use the status code to inform the result of our method. We return 200 if the method executes without any errors, and 500 when there are any error in the processing. Last, but not least, we spit the log of the operation in the response body, so the client knows what happened in the method execution and there you are! We have REST...
Please, stop!
RESTful for the win
I'm sure that you have read a lot of tutorials about REST, status codes, http verbs and everything else. But it's time to stop memorizing REST and start thinking REST.
REST is not a protocol (HTTP is). REST is not a specific technology communication (RMI is). REST is an abstraction over a protocol, it's a modern web architecture, thought to replace the specific technology communication protocols and define a way of integrating systems with very loose coupling and much more versatility.
Much more than that, REST is a communication way where the communicators (the systems) are not being orchestrated by a conductor. It is more like a dance, where the dancers know what they should do to make the dance works and be beautiful.
If you are using REST just as a communication protocol, stop calling it REST and start calling it "HTTP Interface", it's better.
Hyping Hypermedia
When we talk about REST, we are talking about Hypermedia. Period. I totally agree with Steve Klabnik in his post Rest is Over. Steve says that RESTful APIs have evolved to Hypermedia APIs. As it should be from the begining.
REST isn't only about communication by HTTP requests, correct HTTP verbs or well-chosen status codes, the real thing is Hypermedia.
Formally we have four constraints in REST:
- Identification of resources;
- Manipulation of resources through representations;
- Self-descriptive messages;
- Hypermedia as the engine of application state;
In my experience I've seen that constraints one and two are easier to understand and use. Constraint three is often misunderstood and not well implemented. Constraint four, almost always, is left behind. But what does "Hypermedia as the engine of application state" mean?
Well, it means that you can look to your application as a finite-state machine, where the actual node represents the current resource being "viewed" by the user, and the transitions are like instructions to the user on his next steps.
Let's take a look at an example. Imagine that we have an online payment system, responsible for managing transactions between sellers and buyers from a lot of other services (have you heard about any services like this?).
Imagine that Bob wants to buy a bycicle from Bikers World website. The first thing that the website should do is create a payment resource using the RESTful API of our payment service. It can be something like:
POST /payments
Host: bikersworld.com
Accept: application/json
Request-Body:
{
"transactionId": "hyx48yu9pe",
"value": "150.0"
}And then our server responds something like this:
HTTP/1.1 204 CREATED
Content-Type: application/json
Response-Body:
{
"transactionId": "hyx48yu9pe",
"value": "150.0",
"status": "pending",
"links": [
{
"rel": "self",
"method": "get",
"href": "http://onlinepayments.com/payments/5"
},
{
"rel": "confirm",
"method": "put",
"href": "http://onlinepayments.com/payments/5/confirm"
},
{
"rel": "cancel",
"method": "delete",
"href": "http://onlinepayments.com/payments/5"
}
]
}Did you notice the "links" key in the json that the API answered? It informs us about the other possible states we can reach from where we are. Would you need to check the API docs to know what you should do next? What would you do if you wanted to cancel the order? Or to retrieve the order info?
As you can see, the server request is enough to inform the user about the next states available to the resource. After creating a payment, it's easy to see that there is a requirement to confirm it, and you know all of this without reading any documentation.
Another thing that can make our API even better is to use the OPTION verb to serve to our clients the options (duh!) that they have for a resource. Imagine an JSON restul API that for a OPTION request like this:
OPTION /payments Host: bikersworld.com Accept: application/json
It returns a JSON documentation like that:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Response-Body:
{
"POST": {
"description": "Create an payment",
"parameters": {
"transactionId": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The transaction id associated to the payment",
"required": true
},
"value": {
"type": "double",
"description": "The value of the payment being created"
"required": true
}
},
"example": {
"transactionId": "hyx48yu9pe",
"value": "150.0"
}
},
... //more useful information
}
I'm not saying that it is easy to apply this concepts and sometimes your domain can't be mapped very well to a state-driven model and your entities don't have a well defined lifecycle. In this case you should try to do your best to fit these concepts in your API.But don'let hypermedia overwhelm you. You can develop your API incrementally. In this post, Matt Cottingham showed a picture that I consider to be an excelent representation of the steps taken by an API during it's development.
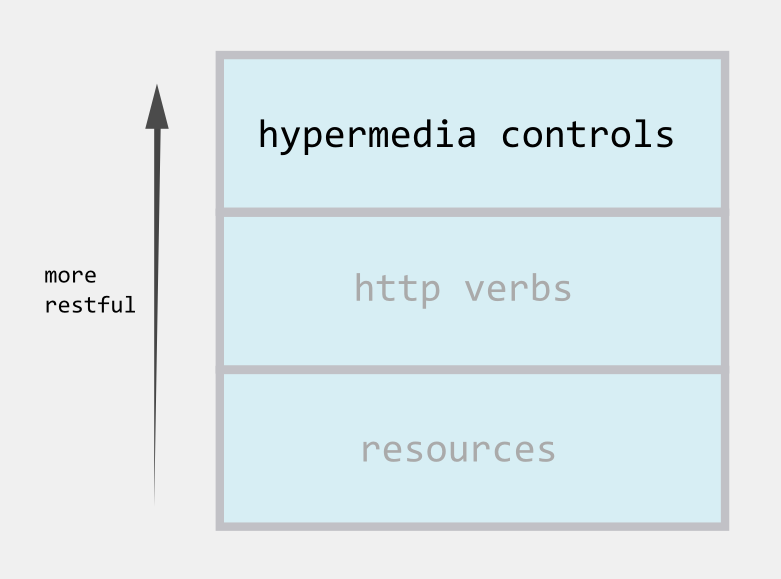
As you can see, hypermedia controls are labeled as the top level feature for a restful API, but this doesn't mean that you can't design a restful (not THAT restful) API without it. You can, but don't forget this image. As any software, our API definitions can evolve and be more restful day by day.
Useful resources:
- Principled Design of the Modern Web Architecture, article written by Roy T. Fielding and Richard N. Taylor;
- Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures, PhD thesis written by Roy T. Fielding;
- PUT or POST: The REST of the Story, blog post by John Calcote;
- A Short Explanation of Hypermedia Controls in RESTful Services, blog post by Matt Cottingham;
- REST APIs must be hypertext-driven blog post by Roy T. Fielding;
- Why HATEOAS, presentation by Wayne Lee;
- The RESTful CookBook, created by Joshua Thijssen;
- The HTTP OPTIONS method and potential for self-describing RESTful APIs, blog post by Zac Stewart;
- Netflix Rest API documentation, an awesome example of restful API.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments